Description
Austral Indigo
Common names
Austral Indigo, Hill Indigo, Native Indigo, Australian Indigo, New Holland Indigo.
Scientific names
Indigofera australis.
Family
Fabaceae.
Genus
Indigofera.
Name origin
Indigofera, neo-Latin for indigo-bearing. Australis, Latin for southern.
Rainfall
300mm+.
Growth rate
Fast.
Growth height
Up to 2.5m.
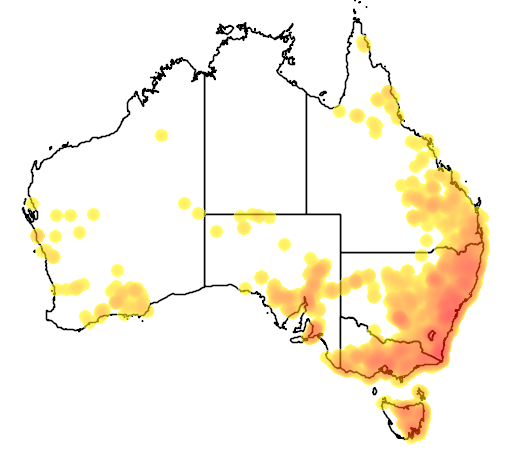
Presence in Australia
Widespread. Noted in most areas across region.
This specie has been identified in the following Australian states: Qld, NSW, ACT, Vic, Tas, SA, WA.
Habitat
Woodland and eucalypt forest. Commonly hilly areas.
Habit
Open erect spreading shrub to 2.5m high. Long slender stiff stems.
Site preference
Poor, shallow soil in semi or dappled shade. Tolerates moderately heavy frost and extended wet periods. Adapts to most well-drained acidic soils.
Characteristics
Palatable, nutritious legume, grazed severely by livestock.
Flowering
Mauve to purple (sometimes white), winter-spring. Pea-like.
Seed collection
Mid Nov to early Feb. Monitor closely as seeds shed immediately or very soon after maturity. Ensure collection by securing nylon stockings or paper bags to fruiting branches after flowering.
Propagation
From scarified seed or cuttings. Pour boiling or very hot water over seeds and soak until water cools. Dry to prevent rotting and sow. Germination takes 3-4 weeks. Suitable for direct seeding in pots (2-3 seeds per pot).
Regeneration
From seed, particularly after fire. Establishes readily when direct seeded.
Shade and shelter
Useful low-level cover in windbreaks.
Land protection
Legume - improves soil fertility by "fixing" nitrogen.
Wildlife
Excellent habitat. Flowers are a pollen and nectar source for many native insects, including bees and wasps. Also food for butterfly caterpillars.
Koori
Roots hammered and placed in salt or fresh water to poison fish.
Ornamental
Attractive ornamental, particularly when flowering. Plant in groups for best effect. Tip prune from when young to promote bushiness and prevent straggliness. Cut dead or straggly branches at base. Coppices.
Other
Leaves and stems produce yellow-fawn dye with alum as mordant.