Description
Common names
Eurabbie, Blue Gum, Southern Blue Gum, Victorian Blue Gum.
Scientific names
Eucalyptus bicostata, Eucalyptus globulus subsp. bicostata.
Family
Myrtaceae.
Genus
Eucalyptus.
Name origin
Bicostata, from the Latin bi, two, plus costatus, ribbed, referring to the two ridges commonly on the buds and fruits.
Rainfall
700-1200mm.
Growth rate
Fast.
Growth height
Up to 40m.
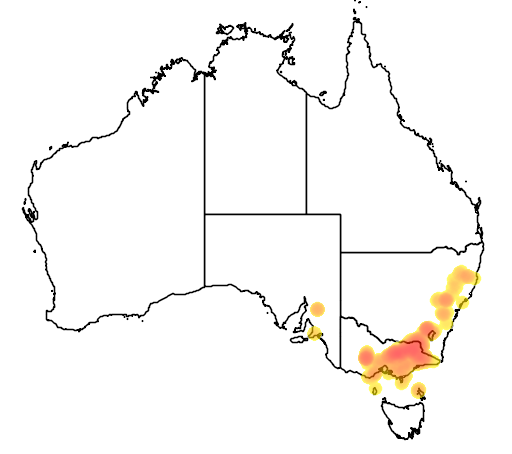
Presence in Australia
Primarily in wetter areas east of Hume Highway and south of Murrumbidgee catchments.
This specie has been identified in the following Australian states: NSW, ACT, Vic, SA.
Habitat
Fertile soils in sheltered areas, in wet forest.
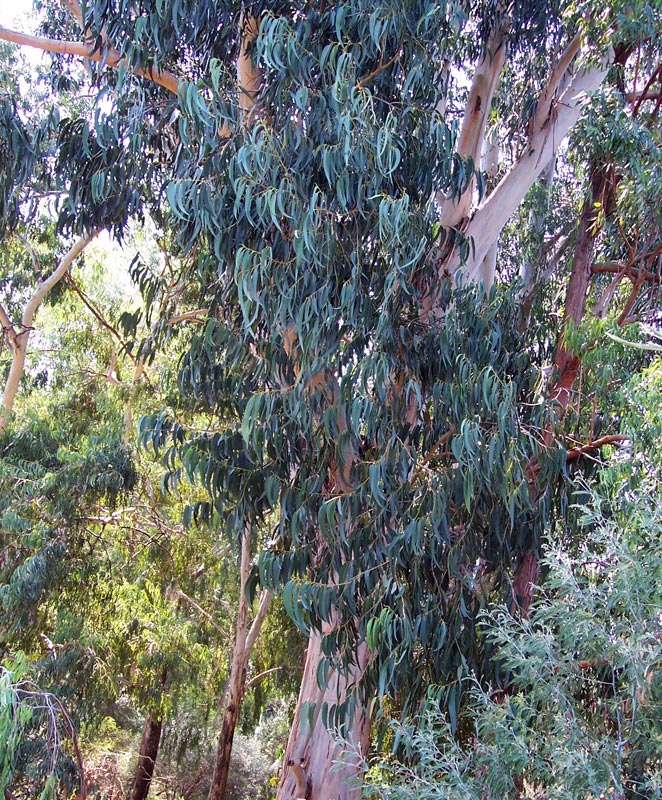
Habit
Tree to 40m high with smooth white or grey bark, shedding in ribbons, and long narrow glossy green adult leaves.
Site preference
Moist, relatively heavy, fertile soil. Tolerates poorly-drained and boggy soil. Seedlings are susceptible to frost.
Characteristics
Grows very rapidly when young. Uses large volumes of water, and if grown outside its natural range, summer water shortages may lead to tree death. Responds to fertiliser.
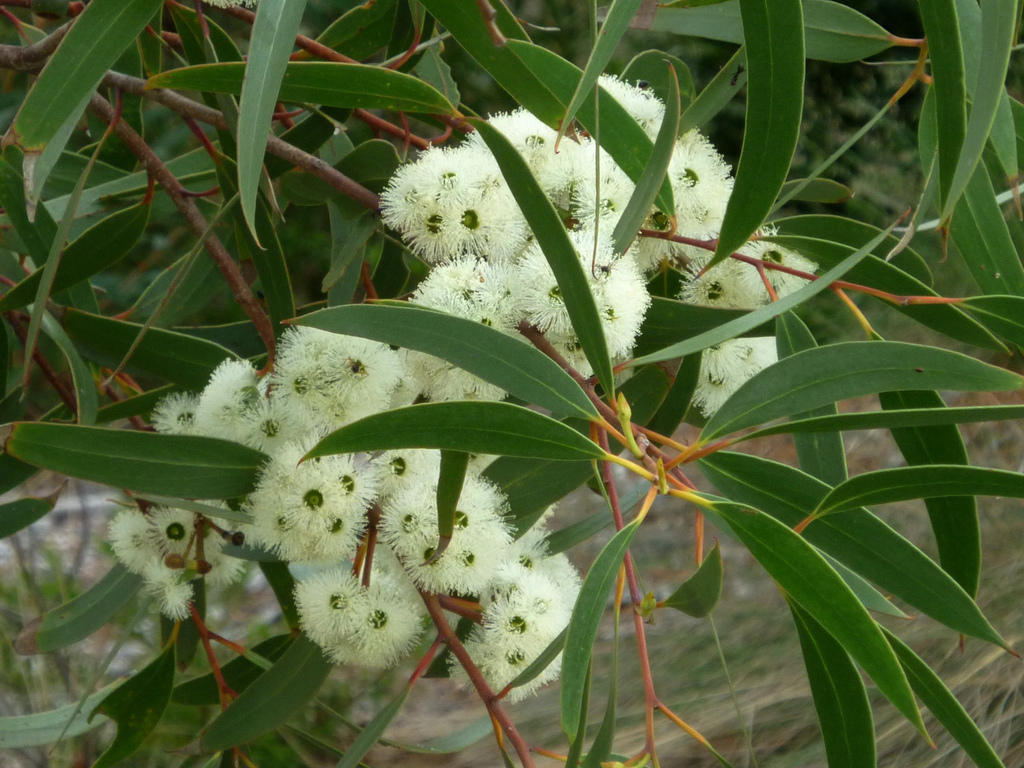
Flowering
White-cream, Sep-Jan.
Seed collection
Early Jan to late May.
Propagation
From seed (±109 viable seeds per gram). Optimum germination temperature 270C.
Regeneration
From seed, under during favourable seasons such as wet summers, particularly in absence of competitive exotic grasses. Coppices after fire or cutting.
Shade and shelter
Useful high-level cover in windbreaks. Casts heavy shade which suppresses most other vegetation.
Land protection
Useful in gully erosion control, behind fibrous-rooted understorey plants.
Fuel
Moderate. Forms good coals and few sparks. Rates fair in splitting and ignitability.
Timber
Strong, moderately durable, with light-yellow or brown heartwood. Usually has interlocked grain with distinct growth rings. Density about 900 kg/m3. Mainly used in general construction, for making tool handles, and in bridges. Was used for cross-arms in electricity poles. Increasingly used as feature timber. Sapwood susceptible to damage by Lyctus borers. Can be grown for hardwood pulp or sawlogs. Useful as quick-growing "nurse" crop for Blackwood (Acacia melanoxylon) which benefits from shelter.
Wildlife
Nectar-rich flowers food for various insects and nectar-feeding birds. Fruit and seeds eaten by lorikeets, parrots and rosellas. Foliage important koala food. Hollows nesting sites for many birds and mammals. Important food source for the Yellow-bellied Glider.
Ornamental
Useful in parklands where a dense stand required quickly. Generally unsuitable for smaller gardens. Sometimes seen as untidy because its fallen leaves and twigs are slow to decompose. Suppresses most other vegetation.
Other
Leaves were used in a range of treatments including croup, asthma and colds as a vapour inhalation, and as an insecticide powder or spray. Leaves produce orange-tan dye with mordant alum.