Description
Common names
Silver Wattle, Silver Wattle., Silves Wattle.
Scientific names
Acacia dealbata.
Family
Mimosaceae.
Genus
Acacia.
Name origin
From Latin dealbatus, white-washed, referring to the young white shoots and leaves.
Rainfall
650mm.
Growth rate
Fast, very fast.
Growth height
6-15m.
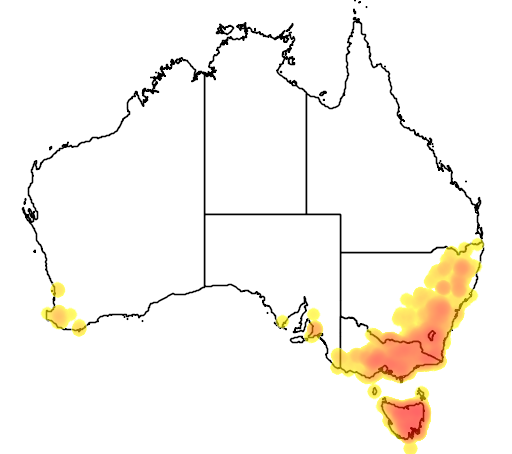
Presence in Australia
Widespread, in all catchments and districts.
This specie has been identified in the following Australian states: Qld, NSW, ACT, Vic, Tas, SA, WA.
Habitat
Usually dry sclerophyll forest on a variety of soils, often on slopes and creek banks.
Habit
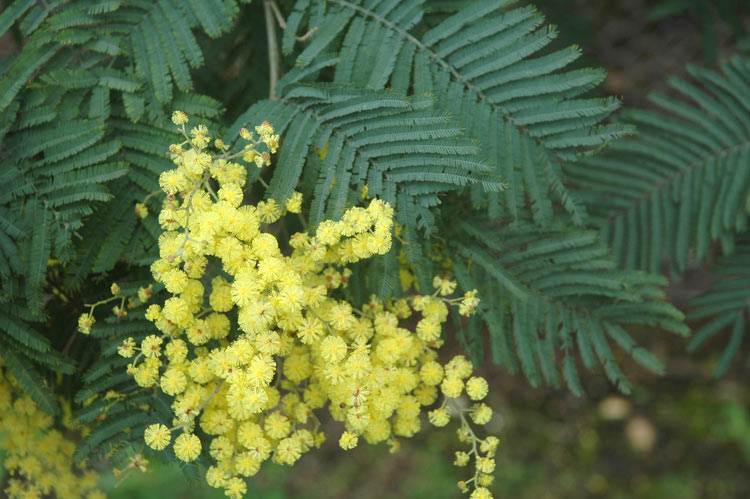
Erect tree, 6-15m high with smooth to deeply fissured dark grey to almost black bark, and silvery grey to greenish feathery foliage.
Similar species
Distinguished from Black Wattle (A. mearnsii) by its lighter foliage and trunk, and earlier flowering (Jul-Nov), while Black Wattle flowers around Oct-Dec. Silver Wattle has glands at the base of each pinna, while Black Wattle and Northern Silver Wattle (A. leucoclada) have glands all along the leaf stem.
Site preference
Soils moist for part of year but not waterlogged, especially stream sides. Tolerates drier soils such as granite slopes. Tolerates strong wind, moderate frost and snow. Resents poorly drained or permanently wet soil.
Characteristics
Very fast growing. Lifespan up to several decades. Matures early, setting seed at 4-5 years of age. Prone to gall rusts, caterpillar and borer activity. Seeds persist in soil for around 50 years. Fire retarder.
Flowering
Golden-yellow, Jul-Nov. Prolific and perfumed.
Seed collection
Nov-Jan, depending on season. Produces large seed crops every 2-3 years. Monitor closely, as seeds dropped soon after maturity.
Propagation
From scarified seed (45-84 viable seeds per gram). Pour boiling water over seeds and soak for several hours before sowing.
Regeneration
From seed or suckers, particularly after fire, ploughing or ripping. Often forms fire-induced thickets. Regenerates well from cut stumps and coppices from dormant buds under bark after cutting or burning. Establishes well when direct-seeded. Palatable to stock.
Shade and shelter
Useful fast-growing species for medium-level cover in windbreaks. Suckering ensures cover beyond the life of individual plants. Fast growth and ability to improve soil fertility make it an ideal "nurse crop", and suitable to be used with slow-growing eucalypts or other long-lived species in mixed woodlots.
Land protection
Excellent for controlling gully erosion. Provides fast cover through its growth and suckering. Legume, improves soil fertility through "fixing" nitrogen.
Fuel
Fast-burning, but poor compared to other wattles.
Timber
Light brown to pinkish, suitable for glueing and pulping. Density about 710 kg/m3. Small quantities used for producing pulp in Vic and Tas. Easily split and relatively tough, it was used for furniture, clothes pegs, shoe heels, wood wool and producing gum arabic. Valuable for turning or small furniture items, and is used for cabinet work in Tas. Tan bark has moderate levels of tannin for hide or fabric tanning; grown in South Africa for this purpose.
Wildlife
Excellent habitat. Attracts seed-eating birds including rosellas and cockatoos, and insect-eating birds including the Scrubwren. Many species of beetles and their larvae feed on the foliage. Ants seek the funicles (ovule or seed stalks) of fallen seed. Crimson Rosellas eat the half-ripe seed pods. The White-plumed Honeyeater sometimes nests in the foliage. Critical habitat for gliders and possums, and the gum is a favoured food of the Sugar Glider and Squirrel Glider. Provides structural diversity for nesting and foraging, and is a critical component of streamside vegetation in the region.
Koori
Wood used for stone axe handles, and gum used to fasten head to handle. Also used for boomerangs. Gum eaten, or dissolved in water with nectar to make sweet drink. Bark infusions in hot water drunk as remedy for indigestion.
Ornamental
Silvery foliage and prolific flowers make ideal specimen for parks and gardens. Suckering may cause problems in smaller gardens. Resents pruning and suckers if cut back severely. Useful shade and screening.
Other
Leaves produce yellow-fawn dye with alum as mordant, and green dye with chrome and copper. Widely grown overseas. In Europe its flowers sold as "mimosa". Gum highly soluble in water, and was reputedly dissolved in boiling milk and taken for dysentery and diarrhoea, with good results, by European settlers.